DeepSleep GPIO PWM Wakeup¶
1 功能概述¶
本例程演示如何使 SoC 进入 DeepSleep 状态,然后使用外部 PWM 波形通过 GPIO 将其唤醒。
2 环境准备¶
硬件设备与线材:
PAN107X EVB 核心板与底板各两块
JLink 仿真器(用于烧录例程程序)
逻辑分析仪(Logic Analyzer, LA,用于观察 PWM 波形信息和 GPIO 中断信息)
电流计(本文使用电流可视化测量设备 PPK2 [Nordic Power Profiler Kit II] 进行演示)
USB-TypeC 线一条(用于底板供电和查看串口打印 Log)
杜邦线数根或跳线帽数个(用于连接各个硬件设备)
硬件接线(本例程):
将其中一块 EVB 核心板插到其中一块底板上
为确保能够准确地测量 SoC 本身的功耗,排除底板外围电路的影响,请确认 EVB 底板上的:
Voltage 排针组中的 VCC 和 VDD 均接至 3V3
POWER 开关从 LDO 档位拨至 BAT 档位(并确认底板背部的电池座内没有纽扣电池)
使用 USB-TypeC 线,将 PC USB 插口与 EVB 底板 USB->UART 插口相连
使用杜邦线将 EVB 底板上的 TX 引脚接至核心板 P16,RX 引脚接至核心板 P17
使用杜邦线将 JLink 仿真器的:
SWD_CLK 引脚与 EVB 底板的 P00 排针相连
SWD_DAT 引脚与 EVB 底板的 P01 排针相连
SWD_GND 引脚与 EVB 底板的 GND 排针相连
将逻辑分析仪硬件的:
USB 接口连接至 PC USB 接口
三个通道的信号线分别连接至 EVB 底板的 P13 / P14 / P15 排针
GND 连接至 EVB 底板的 GND 排针
将 PPK2 硬件的:
USB DATA/POWER 接口连接至 PC USB 接口
VOUT 连接至 EVB 底板的 VBAT 排针
GND 连接至 EVB 底板的 GND 排针
硬件接线(PWM Waveform Generator 例程):
参考 DeepSleep PWM Waveform Generator 例程中的介绍搭建 PWM 波形输出环境
将 PWM 波形输出例程的 P03 引脚与 GPIO 唤醒例程的 P13 引脚相连
将 PWM 波形输出例程的 P04 引脚与 GPIO 唤醒例程的 P14 引脚相连
PC 软件:
串口调试助手(UartAssist)或终端工具(SecureCRT),波特率 921600(用于接收串口打印 Log)
Logic(用于配合逻辑分析仪抓取 IO 波形)
nRF Connect Desktop(用于配合 PPK2 测量 SoC 电流)
3 编译和烧录¶
例程位置:<PAN10XX-NDK>\01_SDK\nimble\samples\low_power\deepsleep_gpio_pwm_wakeup\keil_107x
双击 Keil Project 文件打开工程进行编译烧录,烧录成功后断开 JLink 连线以避免漏电。
4 例程演示说明¶
PC 上打开 PPK2 Power Profiler 软件,供电电压选择 3300 mV,然后打开供电开关
从串口工具中看到如下的打印信息:
Try to load HW calibration data.. DONE. - Chip Info : 0x1 - Chip CP Version : 255 - Chip FT Version : 7 - Chip MAC Address : E110000052E3 - Chip UID : 060300465454455354 - Chip Flash UID : 4250315A3538380B00CE12435603C678 - Chip Flash Size : 512 KB [I] App started.. [I] Wait for Task Notifications..
将 PWM 波形输出板卡上电,使能 PWM 输出,此时观察 GPIO 唤醒例程的 Log,可以看到触发了多次的唤醒过程:
[I] [Uptime: 1931 ms] GPIO P14 IRQ triggered. [I] A notification received, value: 1. [I] Wait for Task Notifications.. [I] [Uptime: 1938 ms] GPIO P14 IRQ triggered. [I] A notification received, value: 1. [I] Wait for Task Notifications.. [I] [Uptime: 1945 ms] GPIO P14 IRQ triggered. [I] A notification received, value: 1. [I] Wait for Task Notifications.. [I] [Uptime: 1950 ms] GPIO P13 IRQ triggered. [I] A notification received, value: 1. [I] Wait for Task Notifications.. [I] [Uptime: 1953 ms] GPIO P14 IRQ triggered. [I] A notification received, value: 1. ...
此时观察芯片电流波形,可以更清晰地看出芯片多次睡眠唤醒的切换过程:
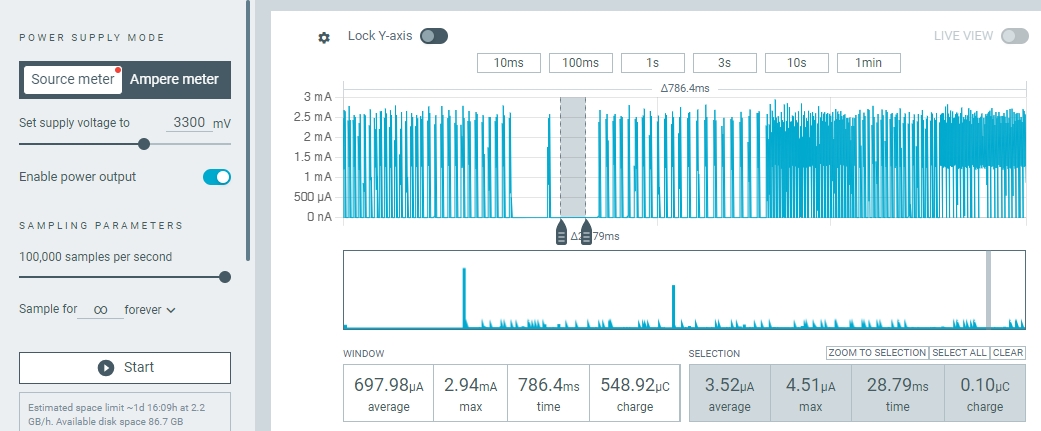
系统被外部 PWM 波唤醒电流波形¶
再观察逻辑分析仪波形,可以看出 GPIO P13/P14 分别被各自输入的 PWM 波形的上升沿唤醒并触发中断:
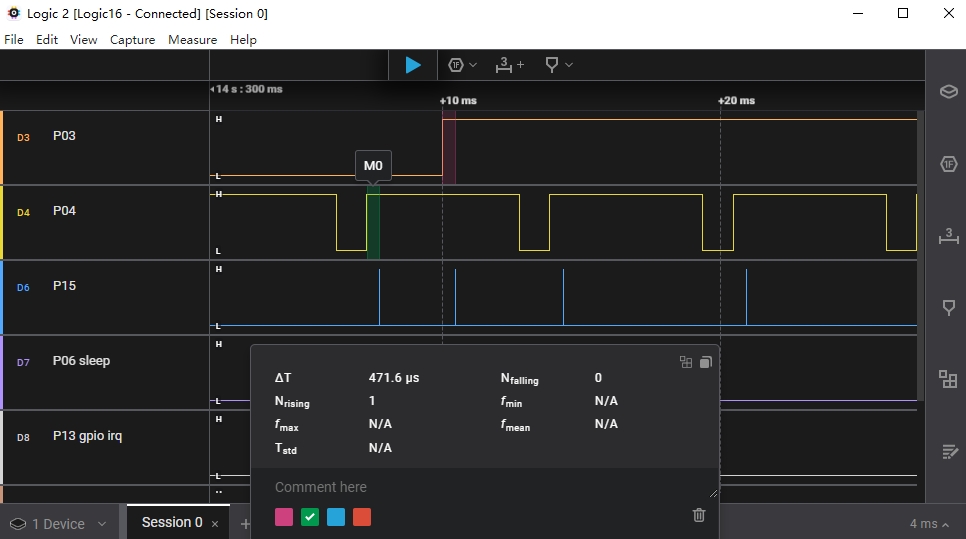
系统被外部 PWM 波唤醒LA波形¶
程序中的两个 GPIO 均被配置为上升沿唤醒,从 LA 波形中可以看出,两个 IO 中的任意一个检测到 GPIO 上升沿,均在短时间内(一般在500us左右)触发芯片唤醒并执行 GPIO 中断(由 P15 引脚指示)
5 开发者说明¶
5.1 SDK Config 配置¶
与本例程相关的 SDK Config (sdk_config.h) 配置有:
Platform Config : Chip Power Mode
芯片供电选择 DCDC 模式,以降低芯片动态功耗
对应宏配置
CONFIG_SOC_DCDC_PAN1070 = 1
LowPower Enable
使能系统低功耗功能
对应宏配置
CONFIG_PM = 1
5.2 程序代码¶
5.2.1 主程序¶
本例程中,OS 为使能状态,因此主程序 main() 函数也是 OS Main Task 的入口函数,其内容如下:
int main(void)
{
/* Application initialization */
app_setup();
/* Application main infinite loop */
app_main_loop();
return 0;
}
5.2.2 App Setup 初始化¶
App 初始化 app_setup() 函数内容如下:
void app_setup(void)
{
APP_LOG_INFO("App started..\n\n");
/*
* Init specific GPIOs:
* - to input mode for wake up use
* - to output mode for ISR indication use
*/
gpio_init();
}
打印 App 初始化 Log
在 gpio_init() 函数中初始化 GPIO 配置
5.2.3 App Main Task Loop 任务循环¶
App Main Task 循环 app_main_loop() 函数内容如下:
void app_main_loop(void)
{
uint32_t ulNotificationValue;
/* Store the handle of current task. */
xTaskToNotify = xTaskGetCurrentTaskHandle();
if(xTaskToNotify == NULL) {
app_assert("Error, get current task handle failed!\n");
}
while (1) {
APP_LOG_INFO("Wait for Task Notifications..\n");
/*
* Wait to be notified that gpio gpio irq occured. Note the first parameter is pdTRUE,
* which has the effect of clearing the task's notification value back to 0, making
* the notification value act like a binary (rather than a counting) semaphore.
*/
ulNotificationValue = ulTaskNotifyTake(pdTRUE, portMAX_DELAY);
APP_LOG_INFO("A notification received, value: %d.\n\n", ulNotificationValue);
}
}
获取当前任务的 Task Handle,用于后续中断中给次任务发送通知使用
在 while (1) 主循环中尝试获取任务通知(Task Notify),并打印相关的状态信息
5.2.4 GPIO 初始化程序¶
GPIO 初始化程序 gpio_init() 函数内容如下:
static void gpio_init(void)
{
/* Configure GPIO P13/P14 as Rising Edge Interrupt/Wakeup */
/* Set pinmux func as GPIO */
SYS_SET_MFP(P1, 3, GPIO);
SYS_SET_MFP(P1, 4, GPIO);
/*
* Construct GPIO init structure and Init GPIO P13/P14:
* - Set IO to digital input mode
* - Disable internal pull-up resistor
*/
HAL_GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {
.mode = HAL_GPIO_MODE_INPUT_DIGITAL,
.pull = HAL_GPIO_PULL_DISABLE,
};
HAL_GPIO_Init(P1_3, &GPIO_InitStruct);
HAL_GPIO_Init(P1_4, &GPIO_InitStruct);
/* Construct GPIO interrupt init structure */
HAL_GPIO_IntInitTypeDef GPIO_IntInitStruct = {
.intMode = HAL_GPIO_INT_RISING,
.debounce = DISABLE,
};
/* Init GPIO P13 interrupt */
GPIO_IntInitStruct.callbackFunc = gpio_p13_input_callback;
HAL_GPIO_InterruptInit(P1_3, &GPIO_IntInitStruct);
/* Init GPIO P14 interrupt */
GPIO_IntInitStruct.callbackFunc = gpio_p14_input_callback;
HAL_GPIO_InterruptInit(P1_4, &GPIO_IntInitStruct);
/* Enable GPIO IRQ in NVIC */
NVIC_EnableIRQ(GPIO1_IRQn);
/* Configure GPIO P15 to push-pull output mode (with init low level) */
SYS_SET_MFP(P1, 5, GPIO);
GPIO_InitStruct.mode = HAL_GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PUSHPULL;
GPIO_InitStruct.level = HAL_GPIO_LEVEL_LOW;
HAL_GPIO_Init(P1_5, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
使用 HAL GPIO Driver 将 GPIO P13/P14 配置为中断输入模式:
配置 P13 和 P14 引脚 Pinmux 至 GPIO 功能(此步骤可省略,原因是这两个引脚默认就是 GPIO 功能)
使能 P13 和 P14 的数字输入模式,并禁用内部上拉和下拉电阻
使能 P13 和 P14 的中断,将其配置为上升沿触发中断(即上升沿唤醒),并注册中断回调函数
使能 GPIO1 NVIC IRQ
使用 HAL GPIO Driver 将 GPIO P15 配置为推挽输出模式,并初始化为低电平
5.2.5 GPIO 中断回调函数¶
static void gpio_p13_input_callback(HAL_GPIO_IntMode intMode)
{
BaseType_t xHigherPriorityTaskWoken = pdFALSE;
if (intMode == HAL_GPIO_INT_RISING) {
/* Notify the task that P13 rising edge detected. */
vTaskNotifyGiveFromISR(xTaskToNotify, &xHigherPriorityTaskWoken);
/* Toggle IO P15 */
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(P1_5, HAL_GPIO_LEVEL_HIGH);
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(P1_5, HAL_GPIO_LEVEL_LOW);
APP_LOG_INFO("[Uptime: %d ms] GPIO P13 IRQ triggered.\n", soc_lptmr_uptime_get_ms());
}
/* Yield if xHigherPriorityTaskWoken is true. */
portYIELD_FROM_ISR(xHigherPriorityTaskWoken);
}
static void gpio_p14_input_callback(HAL_GPIO_IntMode intMode)
{
BaseType_t xHigherPriorityTaskWoken = pdFALSE;
if (intMode == HAL_GPIO_INT_RISING) {
/* Notify the task that P14 rising edge detected. */
vTaskNotifyGiveFromISR(xTaskToNotify, &xHigherPriorityTaskWoken);
/* Toggle IO P15 */
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(P1_5, HAL_GPIO_LEVEL_HIGH);
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(P1_5, HAL_GPIO_LEVEL_LOW);
APP_LOG_INFO("[Uptime: %d ms] GPIO P14 IRQ triggered.\n", soc_lptmr_uptime_get_ms());
}
/* Yield if xHigherPriorityTaskWoken is true. */
portYIELD_FROM_ISR(xHigherPriorityTaskWoken);
}
由于使用 HAL GPIO Driver,因此无需实现 GPIO 中断服务程序,而是要为每个 GPIO 引脚实现自己的中断触发 callback
使用
soc_lptmr_uptime_get_ms()接口获取系统的上电时间戳并打印到串口使用 FreeRTOS
vTaskNotifyGiveFromISR()接口向 App Task 发送通知,表示有 GPIO 中断产生(对应按键按下),此接口中xHigherPriorityTaskWoken变量被配置为pdTRUE,表示当中断返回后将会触发线程调度,而对于此例程来说则是重新调度至 App Task 中的ulTaskNotifyTake()处继续执行
5.2.6 与低功耗相关的 Hook 函数¶
本例程还用到了 2 个与低功耗密切相关的 Hook 函数:
/*
* User can add additional code here right before SoC entering DeepSleep Mode.
* For example:
* - Hardware communication modules' (such as UART/SPI/I2C) Tx/Rx FIFO can be
* checked here to makesure all data in FIFOs have been timely processed.
* - IO pins that are configured as Digital Input Mode are better to switched to
* Analog Mode to avoid current leakage in lowpower mode.
*/
CONFIG_RAM_CODE void vSocDeepSleepEnterHook(void)
{
// This hook function executes right before SoC entering DeepSleep Mode.
#if PAN_LOG_ENABLE && CONFIG_UART_LOG_ENABLE
// Busy wait until all data in log uart tx fifo have been sent out
// to avoid log data loss.
log_uart_wait_tx_done();
#endif
}
/*
* User can add additional code here right after SoC waking up from DeepSleep Mode.
* For example:
* - IO pins that was switched to Analog Mode can be re-configured back to Digital
* Input Mode for properly working.
*/
CONFIG_RAM_CODE void vSocDeepSleepExitHook(void)
{
// This hook function executes right after SoC waking up from DeepSleep Mode.
}
上述两个 Hook 函数用于在进入 DeepSleep 前和从 DeepSleep 唤醒后做一些额外操作,如关闭某些 GPIO 的数字输入功能,以防止 DeepSleep 状态下 GPIO 漏电
详细解释请参考 DeepSleep GPIO Key Wakeup 例程中的相关介绍