Driver: SPI Master¶
1 功能概述¶
该sample演示了SPI作为Master对开发板上的SRAM进行读写操作。
2 环境要求¶
PAN1080 EVB一块
Micro USB线一条(用于供电和查看串口打印Log)
硬件接线:
使用USB线,将PC USB与EVB MicroUSB(USB->UART)相连
使用杜邦线或跳线帽将EVB上的:
UART1 TX与P06相连
UART1 RX与P07相连
PC软件: 串口调试助手(UartAssist)或终端工具(SecureCRT),波特率921600
3 编译和烧录¶
例程位置:zephyr\samples_panchip\drivers\spi_master
目前可使用ZAL工具或quick build脚本进行编译和下载。
脚本位置:quick_build_samples\drivers\spi_master.bat
打开脚本后默认会编译项目,编译完成时,可输入字符进行后续下载等操作:
Input the keyword to continue:
'b' build 编译项目
'r' make clean and rebuild 重新编译项目
'f' flash download 下载
'e' erase chip 擦除芯片
'o' open project by VS Code 打开 `VS Code`,可查看源码,执行编译下载等
others exit 退出
wait input:
4 演示说明¶
连接SPI引脚到SRAM模块(开发板上进行跳线)。
==注:请注意开发板上引脚共用问题,不要将下面四个引脚跳线至其他模块==
引脚
功能
P02
CS
P03
SCK
P30
MOSI
P31
MISO
Sample执行流程:
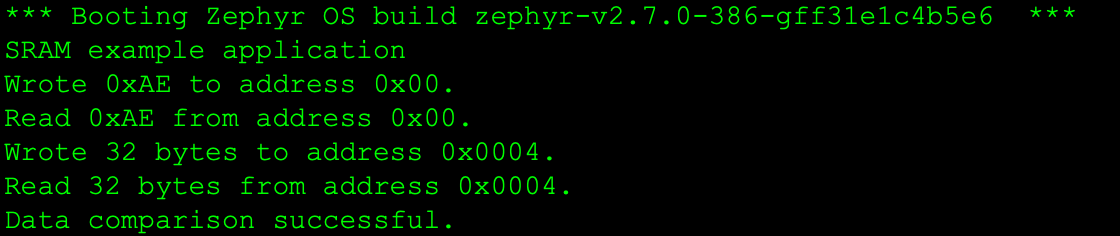
1.写一字节数据【0xAE】到0x00地址
2.从0x00地址读一字节数据
3.写32字节数据到0x0004地址
4.从0x0004地址读32字节数据并和写入数据进行比较,验证读取是否成功
程序正确执行时,日志界面如下(日志中包含Read字样的行表示从Slave读取到的数据):
5 开发说明¶
5.2 初始化SPI¶
const struct device *spi = DEVICE_DT_GET(DT_NODELABEL(spi0));
if (!device_is_ready(spi)) {
printk("SPI device %s is not ready\n", spi->name);
return;
}
5.3 SPI配置¶
可根据实际情况配置即可,需要注意的是参数frequency指的是时钟的分频系数,并非实际的时钟数。例如当前系统外设时钟为16MHz,frequency配置为4,则SPI的时钟速率为16/4=4MHz。
5.4 写操作¶
实现向slave写数据
struct spi_buf bufs[] = {
{
.buf = data,
.len = len
},
};
struct spi_buf_set tx = {
.buffers = bufs,
.count = 1
};
/**
* @brief Write the specified amount of data from the SPI driver.
*
* @note This function is synchronous.
*
* @note This function is an helper function calling spi_transceive.
*
* @param dev Pointer to the device structure for the driver instance
* @param config Pointer to a valid spi_config structure instance.
* Pointer-comparison may be used to detect changes from
* previous operations.
* @param tx_bufs Buffer array where data to be sent originates from.
*
* @retval 0 If successful.
* @retval -errno Negative errno code on failure.
*/
spi_write(spi, spi_cfg, &tx);
5.5 读操作¶
实现从slave读取数据
struct spi_buf bufs[] = {
{
.buf = data,
.len = len
},
};
struct spi_buf_set rx = {
.buffers = bufs,
.count = 1
};
/**
* @brief Read the specified amount of data from the SPI driver.
*
* @note This function is synchronous.
*
* @note This function is an helper function calling spi_transceive.
*
* @param dev Pointer to the device structure for the driver instance
* @param config Pointer to a valid spi_config structure instance.
* Pointer-comparison may be used to detect changes from
* previous operations.
* @param rx_bufs Buffer array where data to be read will be written to.
*
* @retval 0 If successful.
* @retval -errno Negative errno code on failure.
*/
spi_read(spi, spi_cfg, &rx);
5.6 读写操作¶
实现向slave发送数据的同时接收来自slave的数据
struct spi_buf bufs_tx[] = {
{
.buf = data,
.len = len
},
};
struct spi_buf bufs_rx[] = {
{
.buf = data,
.len = len
},
};
struct spi_buf_set tx = {
.buffers = bufs_tx,
.count = 1
};
struct spi_buf_set rx = {
.buffers = bufs_rx,
.count = 1
};
/**
* @brief Read/write the specified amount of data from the SPI driver.
*
* @note This function is synchronous.
*
* @param dev Pointer to the device structure for the driver instance
* @param config Pointer to a valid spi_config structure instance.
* Pointer-comparison may be used to detect changes from
* previous operations.
* @param tx_bufs Buffer array where data to be sent originates from,
* or NULL if none.
* @param rx_bufs Buffer array where data to be read will be written to,
* or NULL if none.
*
* @retval frames Positive number of frames received in slave mode.
* @retval 0 If successful in master mode.
* @retval -errno Negative errno code on failure.
*/
spi_transceive(spi, spi_cfg, &tx, &rx);